ONE/Simple test setup
Contents
Overview
This shows how to use VPP lite to build a simple/toy IP4 LISP overlay on an Ubuntu host using namespaces and af_packet interfaces. The LispFlowMapping Map-Server/Resolver in OpenDaylight Beryllium is used as overlay control plane. Although only IP4 addresses are used throughout the tutorial, they can safely be substituted with IP6 addresses.
Prerequisites
- Ubuntu host with bridge-utils installed
- OpenDaylight Beryllium
- Postman Chrome app (optional)
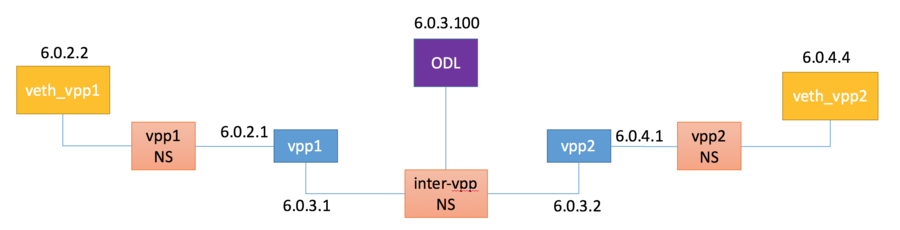
Topology
Setup
This section explains how to build VPP lite and walks through the host, vpp and ODL configs
Build VPP lite
Assuming this is done in a vagrant vm:
cd /vpp export PLATFORM=vpp_lite make build
More details on vpp-lite and other alternative builds can be found in the alternative builds section.
Host
Create namespaces and set up client, vpp and ODL interfaces.
# path to vpp executable and configurations folder
VPP_LITE_BIN=/vpp/build-root/install-vpp_lite_debug-native/vpp/bin/vpp
VPP_LITE_CONF=/etc/vpp/lite/
# make sure there are no vpp instances running
pkill vpp
# delete previous incarnations if they exist
ip netns exec intervppns ifconfig vppbr down
ip netns exec intervppns brctl delbr vppbr
ip link del dev veth_vpp1 &> /dev/null
ip link del dev veth_vpp2 &> /dev/null
ip link del dev veth_intervpp1 &> /dev/null
ip link del dev veth_intervpp2 &> /dev/null
ip link del dev veth_odl &> /dev/null
ip netns del vppns1 &> /dev/null
ip netns del vppns2 &> /dev/null
ip netns del intervppns &> /dev/null
if [ "$1" == "clean" ] ; then
exit 0;
fi
# create vpp to clients and inter-vpp namespaces
ip netns add vppns1
ip netns add vppns2
ip netns add intervppns
# create vpp and odl interfaces and set them in intervppns
ip link add veth_intervpp1 type veth peer name intervpp1
ip link add veth_intervpp2 type veth peer name intervpp2
ip link add veth_odl type veth peer name odl
ip link set dev intervpp1 up
ip link set dev intervpp2 up
ip link set dev odl up
ip link set dev veth_intervpp1 up netns intervppns
ip link set dev veth_intervpp2 up netns intervppns
ip link set dev veth_odl up netns intervppns
# create bridge in intervppns and add vpp and odl interfaces
ip netns exec intervppns brctl addbr vppbr
ip netns exec intervppns brctl addif vppbr veth_intervpp1
ip netns exec intervppns brctl addif vppbr veth_intervpp2
ip netns exec intervppns brctl addif vppbr veth_odl
ip netns exec intervppns ifconfig vppbr up
# create and configure 1st veth client to vpp pair
ip link add veth_vpp1 type veth peer name vpp1
ip link set dev vpp1 up
ip link set dev veth_vpp1 up netns vppns1
ip netns exec vppns1 \
bash -c "
ip link set dev lo up
ip addr add 6.0.2.2/24 dev veth_vpp1
ip route add 6.0.4.0/24 via 6.0.2.1
"
# create and configure 2nd veth client to vpp pair
ip link add veth_vpp2 type veth peer name vpp2
ip link set dev vpp2 up
ip link set dev veth_vpp2 up netns vppns2
ip netns exec vppns2 \
bash -c "
ip link set dev lo up
ip addr add 6.0.4.4/24 dev veth_vpp2
ip route add 6.0.2.0/24 via 6.0.4.1
"
# set odl iface ip and disable checksum offloading
ifconfig odl 6.0.3.100/24
ethtool --offload odl rx off tx off
# start vpp1 and vpp2 in separate chroot
sudo $VPP_LITE_BIN \
unix { log /tmp/vpp1.log cli-listen \
localhost:5002 full-coredump \
exec $VPP_LITE_CONF/vpp1.conf } \
api-trace { on } chroot {prefix xtr1}
sudo $VPP_LITE_BIN \
unix { log /tmp/vpp2.log cli-listen \
localhost:5003 full-coredump \
exec $VPP_LITE_CONF/vpp2.conf} \
api-trace { on } chroot {prefix xtr2}
vpp1 config
Create and configure the LAN and WAN facing af_packet interfaces
- Create LAN facing
host-vpp1and WAN facinghost-intervpp1interfaces - Set
6.0.2.1/24and6.0.3.1as their respective IP4 addresses
Enable and configure LISP-GPE:
- Set WAN facing interface
host-vpp1as locator (underlay attachment point) - Set LAN facing prefix
6.0.2.0/24as a local EID (End-host ID - overlay address) - Configure map-server address
6.0.3.100
vpp1.conf script should look like this:
create host-interface name vpp1 set int state host-vpp1 up set int ip address host-vpp1 6.0.2.1/24 create host-interface name intervpp1 set int state host-intervpp1 up set int ip address host-intervpp1 6.0.3.1/24 lisp gpe enable lisp locator-set add ls1 iface host-intervpp1 p 1 w 1 lisp eid-table add eid 6.0.2.0/24 locator-set ls1 lisp map-resolver add 6.0.3.100
vpp2 config
Create and configure the LAN and WAN facing af_packet interfaces
- Create LAN facing
host-vpp2and WAN facinghost-intervpp2interfaces - Set
6.0.4.1/24and6.0.3.2as their respective IP4 addresses
Enable and configure LISP-GPE:
- Set WAN facing interface
host-vpp2as locator (underlay attachment point) - Set LAN facing prefix
6.0.4.0/24as a local EID (End-host ID - overlay address) - Configure map-server address
6.0.3.100
vpp2.conf script should look like this:
create host-interface name vpp2 set int state host-vpp2 up set int ip address host-vpp2 6.0.4.1/24 create host-interface name intervpp2 set int state host-intervpp2 up set int ip address host-intervpp1 6.0.3.2/24 lisp gpe enable lisp locator-set add ls1 iface host-intervpp2 p 1 w 1 lisp eid-table add eid 6.0.4.0/24 locator-set ls1 lisp map-resolver add 6.0.3.100
ODL Map-Server/Resolver
Steps to install and configure ODL, assuming the SR1 tar archive is downloaded:
Install and run ODL
wget https://nexus.opendaylight.org/content/repositories/opendaylight.release/org/opendaylight/integration/distribution-karaf/0.4.1-Beryllium-SR1/distribution-karaf-0.4.1-Beryllium-SR1.tar.gz tar xzf distribution-karaf-0.4.1-Beryllium-SR1.tar.gz cd distribution-karaf-0.4.1-Beryllium-SR1/bin ./karaf
To install LispFlowMapping Map-Server/Resolver, in the karaf console type:
feature:install odl-lispflowmapping-msmr
Give it some time to load all bundles. You can check progress with log:tail and exit from the log with Ctrl-C
Next, use the postman collection found [here] or curl to configure the Map-Server with the overlay to underlay mapping.
Steps to use the postman collection:
- Import the collection to postman
- Configure environment variables
controllerHostandrestconfPortto the IP of the host where ODL is running and8181respectively. - Add vpp1 and vpp2 mappings
- Check that mapings were insterted by checking all database content
Steps to use the cURL collection:
Prepare two json files with the mappings to be inserted. vpp1-mapping.json file for vpp1 can be found lower, for vpp2 create a similar file with eid address set to 6.0.4.0/24 and rloc to 6.0.3.2. Alternatively, you can find the two files [here]
{
"input": {
"mapping-record": {
"recordTtl": 1440,
"action": "NoAction",
"authoritative": true,
"eid": {
"address-type": "ietf-lisp-address-types:ipv4-prefix-afi",
"ipv4-prefix": "6.0.2.0/24"
},
"LocatorRecord": [
{
"locator-id": "ISP1",
"priority": 1,
"weight": 1,
"multicastPriority": 255,
"multicastWeight": 0,
"localLocator": true,
"rlocProbed": false,
"routed": true,
"rloc": {
"address-type": "ietf-lisp-address-types:ipv4-afi",
"ipv4": "6.0.3.1"
}
}
]
}
}
}
Add mappings for the two vpp instances using cURL. For vpp1 do the following:
curl -u "admin":"admin" -H "Content-type: application/json" -X POST \
http://localhost:8181/restconf/operations/odl-mappingservice:add-mapping \
--data @vpp1-mapping.json
Check that the mappings were correctly inserted using:
curl -u "admin":"admin" -H "Content-type: application/json" -X GET \
http://localhost:8181/restconf/config/odl-mappingservice:mapping-database
Test
Assuming all files have been created and ODL has been configured as explained above, execute the host script you've created or the run_lisp_topo.sh script from [here]. If all goes well, you can now test connectivity between the two namespaces with:
ip netns exec vppns1 ping 6.0.4.4
Traffic and control plane message exchanges can be checked with a wireshark listening on the odl interface.