VPP/Segment Routing for IPv6
This example shows how to use the VPP platform for IPv6 segment routing.
Contents
Introduction
Segment routing changes the way packets are forwarded inside a network to enable network operators to have better control on the path followed by the packets.
Segment Routing can be applied to the IPv6 architecture, with a new type of routing extension header. A segment is encoded as an IPv6 address. An ordered list of segments is encoded as an ordered list of IPv6 addresses in the routing extension header. The segment to process is indicated by a pointer in the routing extension header. Upon completion of a segment, the pointer is incremented.
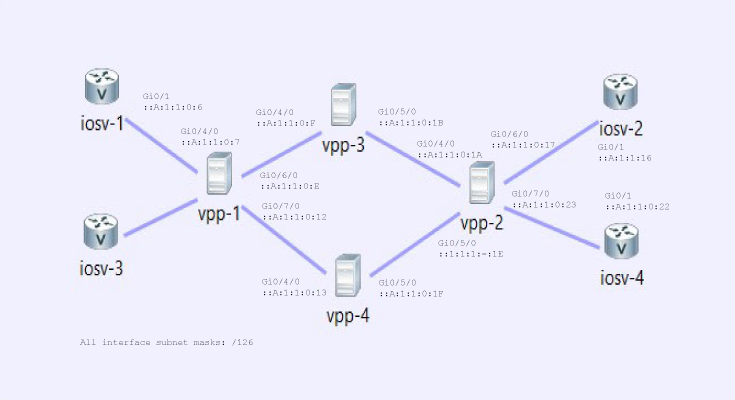
The topology and VPP debug CLI configuration below show how to configure an IPv6 segment routing network.
VIRL File
It can be tedious to configure this scenario manually. For help, see the example:
The example page is a VIRL topology description in plain text. You will need to store the text to a file and give it the .virl extension.
The iosv-1, iosv-2, and iosv-4 nodes are virtual IOS Classic routers, which could be easily replaced with Linux hosts or other network devices capable of sending IPv6 ICMP echo requests.
Topology Diagram
Configuration
iosv-1 relevant configuration
interface GigabitEthernet0/1 description to vpp-1 ipv6 address ::A:1:1:0:6/126 ! route to iosv-2 ipv6 route ::A:1:1:0:16/128 ::A:1:1:0:7 ! route to iosv-4 ipv6 route ::A:1:1:0:22/128 ::A:1:1:0:7
iosv-2 relevant configuration
interface GigabitEthernet0/1 description to vpp-2 ipv6 address ::A:1:1:0:16/126 ! ipv6 route ::A:1:1:0:6/128 ::A:1:1:0:17
iosv-4 relevant configuration
interface GigabitEthernet0/1 description to vpp-2 ipv6 address ::A:1:1:0:22/126 ! Route to iosv-1 ipv6 route ::A:1:1:0:6/128 ::A:1:1:0:23
vpp-1 relevant configuration
set interface ip address GigabitEthernet0/4/0 ::a:1:1:0:7/126 set interface state GigabitEthernet0/4/0 up set interface ip address GigabitEthernet0/5/0 ::a:1:1:0:b/126 set interface state GigabitEthernet0/5/0 up set interface ip address GigabitEthernet0/6/0 ::a:1:1:0:e/126 set interface state GigabitEthernet0/6/0 up set interface ip address GigabitEthernet0/7/0 ::a:1:1:0:12/126 set interface state GigabitEthernet0/7/0 up sr tunnel src 0::a:1:1:0:6 dst 0::a:1:1:0:16/128 next 0::a:1:1:0:f next 0::a:1:1:0:1a next 0::a:1:1:0:16 tag 0::a:1:1:0:7 InPE 1 clean sr tunnel src 0::a:1:1:0:6 dst 0::a:1:1:0:22/128 next 0::a:1:1:0:f next 0::a:1:1:0:1a next 0::a:1:1:0:22 tag 0::a:1:1:0:7 InPE 1 clean
vpp-3 relevant configuration
set interface ip address GigabitEthernet0/4/0 ::a:1:1:0:f/126
set interface state GigabitEthernet0/4/0 up
set interface ip address GigabitEthernet0/5/0 ::a:1:1:0:1b/126
set interface state GigabitEthernet0/5/0 up
comment { to avoid dropping all SR traffic due to source rpf check failures }
ip route add ::a:1:1:0:6/128 via drop
ip route add ::a:1:1:0:16/128 via drop
ip route add ::a:1:1:0:22/128 via drop
vpp-2 relevant configuration
set interface ip address GigabitEthernet0/4/0 ::a:1:1:0:1a/126 set interface state GigabitEthernet0/4/0 up set interface ip address GigabitEthernet0/5/0 ::a:1:1:0:1e/126 set interface state GigabitEthernet0/5/0 up set interface ip address GigabitEthernet0/6/0 ::a:1:1:0:17/126 set interface state GigabitEthernet0/6/0 up set interface ip address GigabitEthernet0/7/0 ::a:1:1:0:23/126 set interface state GigabitEthernet0/7/0 up sr tunnel src 0::a:1:1:0:16 dst 0::a:1:1:0:6/128 next 0::a:1:1:0:1b next 0::a:1:1:0:e next 0::a:1:1:0:6 tag 0::a:1:1:0:17 InPE 1 clean
vpp-4 relevant configuration
set interface ip address GigabitEthernet0/4/0 ::a:1:1:0:13/126 set interface state GigabitEthernet0/4/0 up set interface ip address GigabitEthernet0/5/0 ::a:1:1:0:1f/126 set interface state GigabitEthernet0/5/0 up