Difference between revisions of "VPP/HostStack"
Florin.coras (Talk | contribs) (→Builtin Echo Server/Client) |
(→External Echo Server/Client) |
||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
Then start vpp2 and attach the client: | Then start vpp2 and attach the client: | ||
| − | <code>$ ./build-root/install-vpp_debug-native/vpp/bin/tcp_echo | + | <code>$ ./build-root/install-vpp_debug-native/vpp/bin/tcp_echo client uri tcp://vpp1_ip/port use-svm-api</code> |
Note that use-svm-api option is not needed for the udp_echo app. | Note that use-svm-api option is not needed for the udp_echo app. | ||
Revision as of 01:03, 8 August 2018
Contents
Description
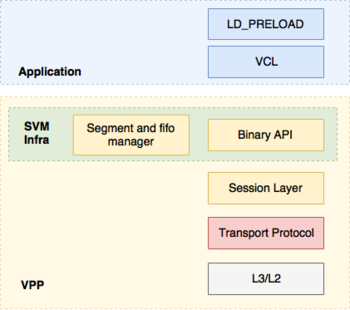
VPP's host stack is a user space implementation of a number of transport, session and application layer protocols that leverages VPP's existing protocol stack. It roughly consists of four major components:
- Session Layer that accepts pluggable transport protocols
- Shared memory mechanisms for pushing data between VPP and applications
- Transport protocol implementations (e.g. TCP, SCTP, UDP)
- Comms Library (VCL) and LD_PRELOAD Library
Documentation
Set Up Dev Environment - Explains how to set up a VPP development environment and the requirements for using the build tools
Session Layer Architecture - Goes over the main features of the session layer
TLS Application - Describes the TLS Application Layer protocol implementation
Getting Started
Applications can link against the following APIs for host-stack service:
- Builtin C API. It can only be used by applications hosted within VPP
- "Raw" session layer API. It does not offer any support for async communication
- VCL API that offers a POSIX-like interface. It comes with its own epoll implementation.
- POSIX API through LD_PRELOAD
A number of test applications can be used to exercise these APIs. For all the examples below, it is assumed that two VPP instances have been brought up and properly configured to ensure networking connectivity between them. To test that network connectivity is available, the builtin ping tool can be used. As a convention, we consider the first vpp instance (vpp1) to be the one the server is attached to and the second instance (vpp2) to be the one where the client application is attached. For illustrative purposes all examples use TCP as a transport protocol but other available protocols could be used.
Builtin Echo Server/Client
On vpp1, from the cli do:
# test echo server uri tcp://vpp1_ip/port
and on vpp2:
# test echo client uri tcp://vpp1_ip/port
For more details on how to further configure the client/server apps to do throughput and CPS testing see here
External Echo Server/Client
To build the external test echo apps first edit vnet.am to make test apps installable
# sed -i 's/noinst_PROGRAMS += tcp_echo udp_echo/bin_PROGRAMS += tcp_echo udp_echo/' src/vnet.am
then build vpp and the apps. Start vpp1 and attach the server application:
$ ./build-root/install-vpp_debug-native/vpp/bin/tcp_echo uri tcp://vpp1_ip/port use-svm-api
Then start vpp2 and attach the client:
$ ./build-root/install-vpp_debug-native/vpp/bin/tcp_echo client uri tcp://vpp1_ip/port use-svm-api
Note that use-svm-api option is not needed for the udp_echo app.
VCL socket client/server
For more details see the tutorial here